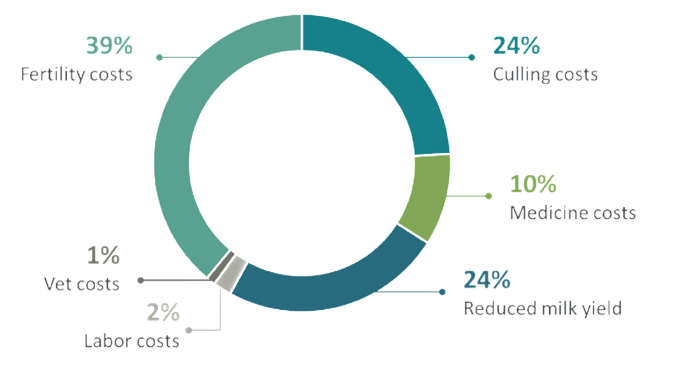Blog | Reading Time 2 minutes
Beneficial bacteria to help maintain hoof health
Lameness in dairy farming is often underestimated. Nowadays, it is estimated that more than 80% of herds are affected by lameness with the number of cows affected globally increasing due to the evolution of housing design.
Today, more than 70% of infectious lameness is due to bacterial infections of the hoof, such as digital dermatitis (or “Mortellaro’s disease”).
We have developed a new preventive solution based on beneficial bacteria, PODO CONCEPT, to help maintain hoof health, and thus ruminant mobility.
Causes and consequences
Lameness causes mobility issues leading to economic losses (Figure 1) and animal welfare problems.
Some of the short-term economic impacts are a reduction in productivity, an increase in veterinary costs, and an increase in labor spent on working with lame cattle.
In the long term, there is an increase in the culling rate (up to 8.4 times more), fertility problems, a reduction in the milk quality (increase in somatic cell count), and an increase in pain and stress experienced by the animals.
On average, more than 50% of the lameness observed is due to infection rather than injury due to trauma or cracks, and most of the infectious cases are digital dermatitis.
Lameness is a multi-factorial disease with several aspects of the housing environment, animal, management, and dietary factors needing to be considered.
According to a scientific consensus, the sooner lameness is detected and addressed, the better the results.
Today’s solutions to address hoof health issues
There are various tools to manage/maintain hoof health, some of which are complementary and work together, but all these actions have their limitations.
- A well-formulated diet. The mixing and feeding of the diet can cause an imbalance in what the animals consume.
- Hoof trimming. If done improperly, hoof trimming can exacerbate pre-existing problems.
- Individual hoof treatments (bandages, antibiotics). These can be constraining and costly.
- Collective/herd treatments. If chemical liquids are used, the efficacy can be reduced by faecal/organic matter. In cold climates, liquids can freeze, and there are health concerns with regular use of hazardous compounds.
Discover our innovative program, PODO CONCEPT!
Watch the video to learn how to use PODO CONCEPT
Published Apr 4, 2023 | Updated May 29, 2023